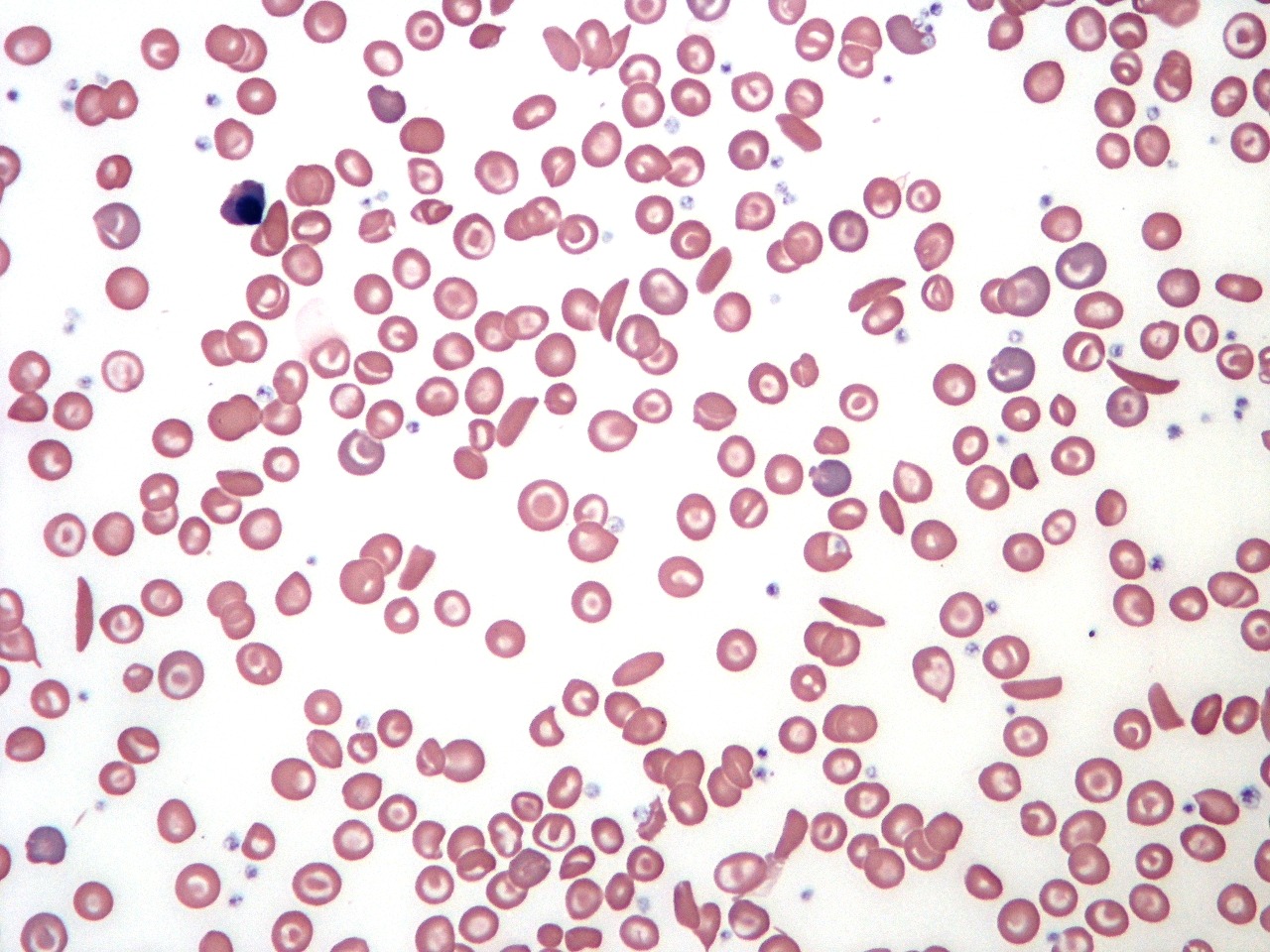
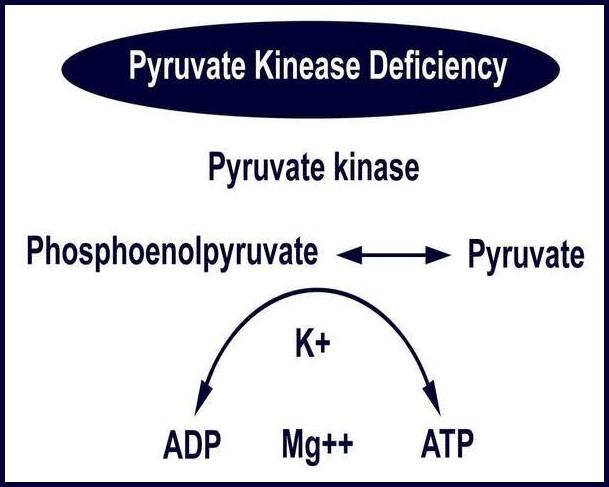
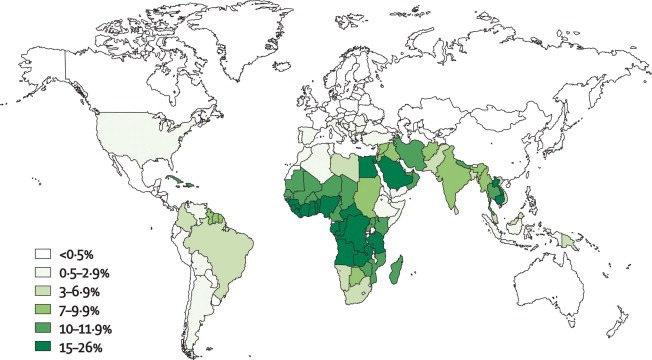
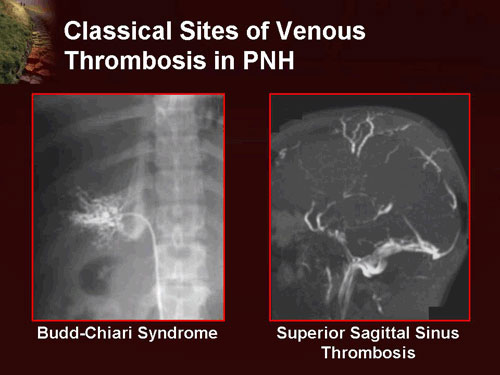
Malaria
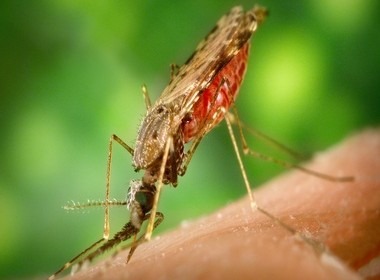
Malaria is a life-threatening parasitic infection caused by protozoa of the Plasmodium genus and transmitted to humans through the bite of an infected female Anopheles mosquito. Once introduced into the bloodstream, the parasite completes a sexual cycle within the mosquito and recurrent asexual cycles in humans, leading to the development of characteristic clinical symptoms. Gametocytes formed in human hosts perpetuate […]
Read more