Hypereosinophilic Syndrome

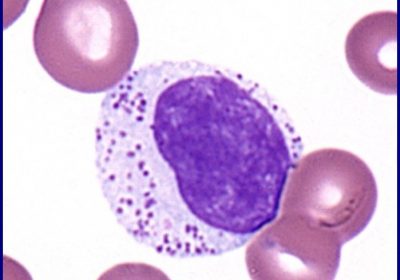
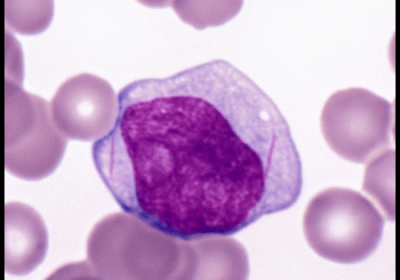
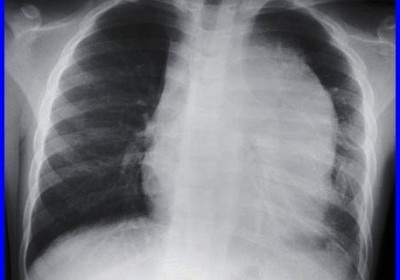
Hypereosinophilic syndrome (HES) is a condition characterized by peripheral blood eosinophilia with manifestations of organ system involvement or dysfunction directly related to eosinophilia in the absence of parasitic, allergic, or other secondary causes of eosinophilia. The ICD 10 code for Hypereosinophilic syndrome [HES] is D72.119. Secondary eosinophilia is a cytokine-derived (interleukin-5 [IL-5]) reactive phenomenon. Worldwide, parasitic diseases are the most […]
Read more