Large Granular Lymphocytic Leukemia
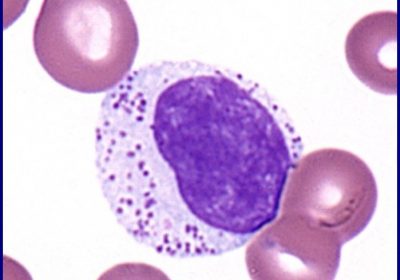
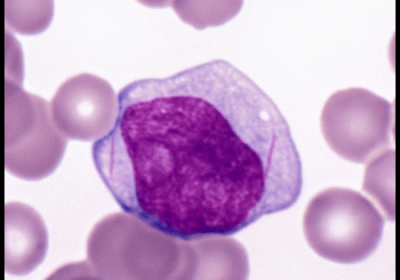
Large granular lymphocytic (LGL) leukemia is a chronic lymphoproliferative disorder characterized by a persistent (>6 months) increase in circulating large granular lymphocytes, typically associated with cytopenias, autoimmune features, and clonal T-cell or NK-cell proliferation. Large granular lymphocytic leukemia is an uncommon condition also described as CD8 lymphocytosis with neutropenia or T-lymphoproliferative disease. Peripheral blood lymphocytosis comprises cells with round or […]
Read more