Malignant Infiltration of Bone Marrow

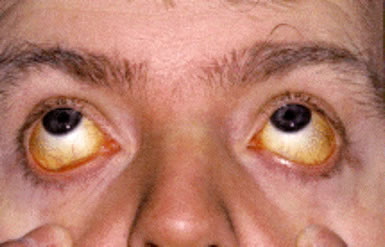
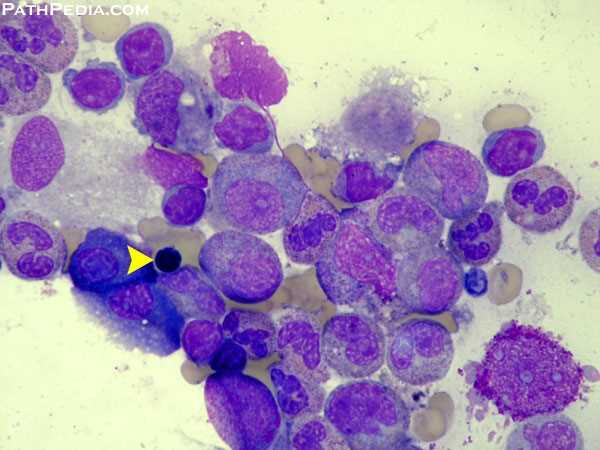
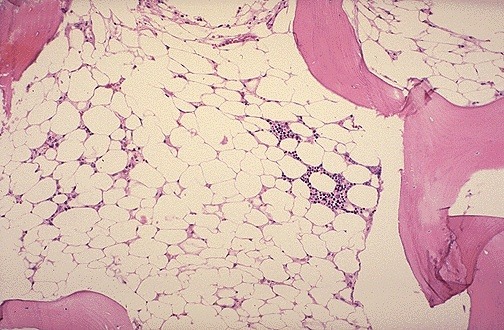
Malignant infiltration of the bone marrow is a significant clinical finding that occurs when solid tumors or hematologic malignancies spread to the marrow space, disrupting normal hematopoiesis. In adults, this process most frequently results from metastatic carcinomas—particularly those originating in the prostate, breast, and lung—although any cancer capable of hematogenous dissemination, including tumors of the colon and thyroid, may […]
Read more