Primary Myelofibrosis
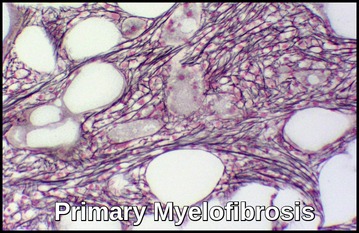
Primary myelofibrosis (PMF) is a chronic myeloproliferative neoplasm characterized by progressive bone marrow fibrosis, extramedullary hematopoiesis, massive splenomegaly, and anemia often accompanied by nucleated red cells and teardrop-shaped erythrocytes. As the spleen and liver enlarge due to compensatory hematopoiesis, patients may develop abdominal discomfort, infarction, portal hypertension, hypersplenism, plasma volume expansion, and an increased risk of splanchnic vein thrombosis. These […]
Read more


