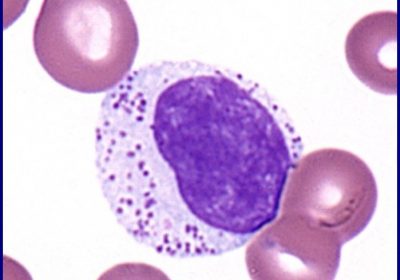
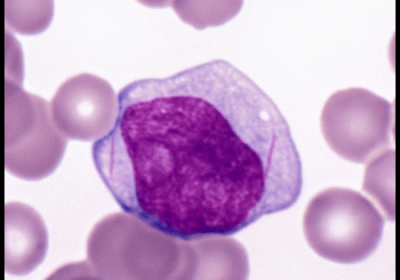
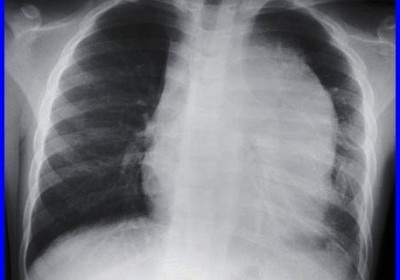
Hypereosinophilic Syndrome

Hypereosinophilic syndrome (HES) is a rare hematologic disorder characterised by persistent eosinophilia in the peripheral blood, typically with an absolute eosinophil count greater than 1.5 × 10⁹/L, leading to organ damage or dysfunction caused by eosinophil-mediated inflammation and tissue infiltration. Unlike secondary eosinophilia due to parasitic infection, allergy, drug reaction, or autoimmune disease, HES is idiopathic or clonal in nature […]
Read more